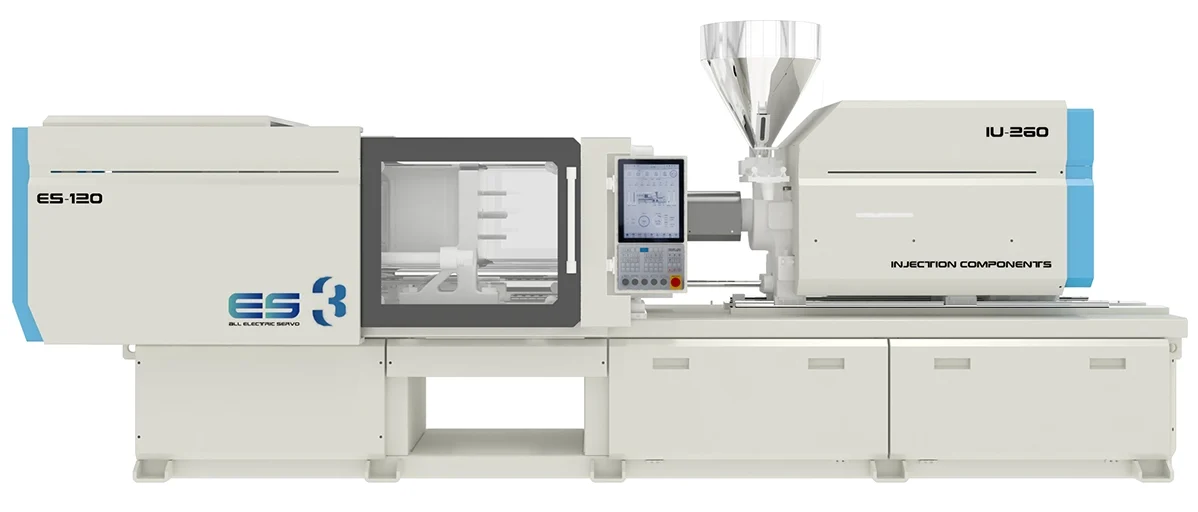
Technical Specifications and Performance
Accurate assessment of the technical specifications of a 120-ton injection molding machine is mandatory for production planning and mold design. This machine class is engineered to deliver a robust balance of throughput and part quality across a defined working envelope.
Key Technical Parameters
These parameters define the machine’s capabilities and constraints, influencing mold design and material selection. The Nominal Configuration represents a typical, well-optimized machine build.
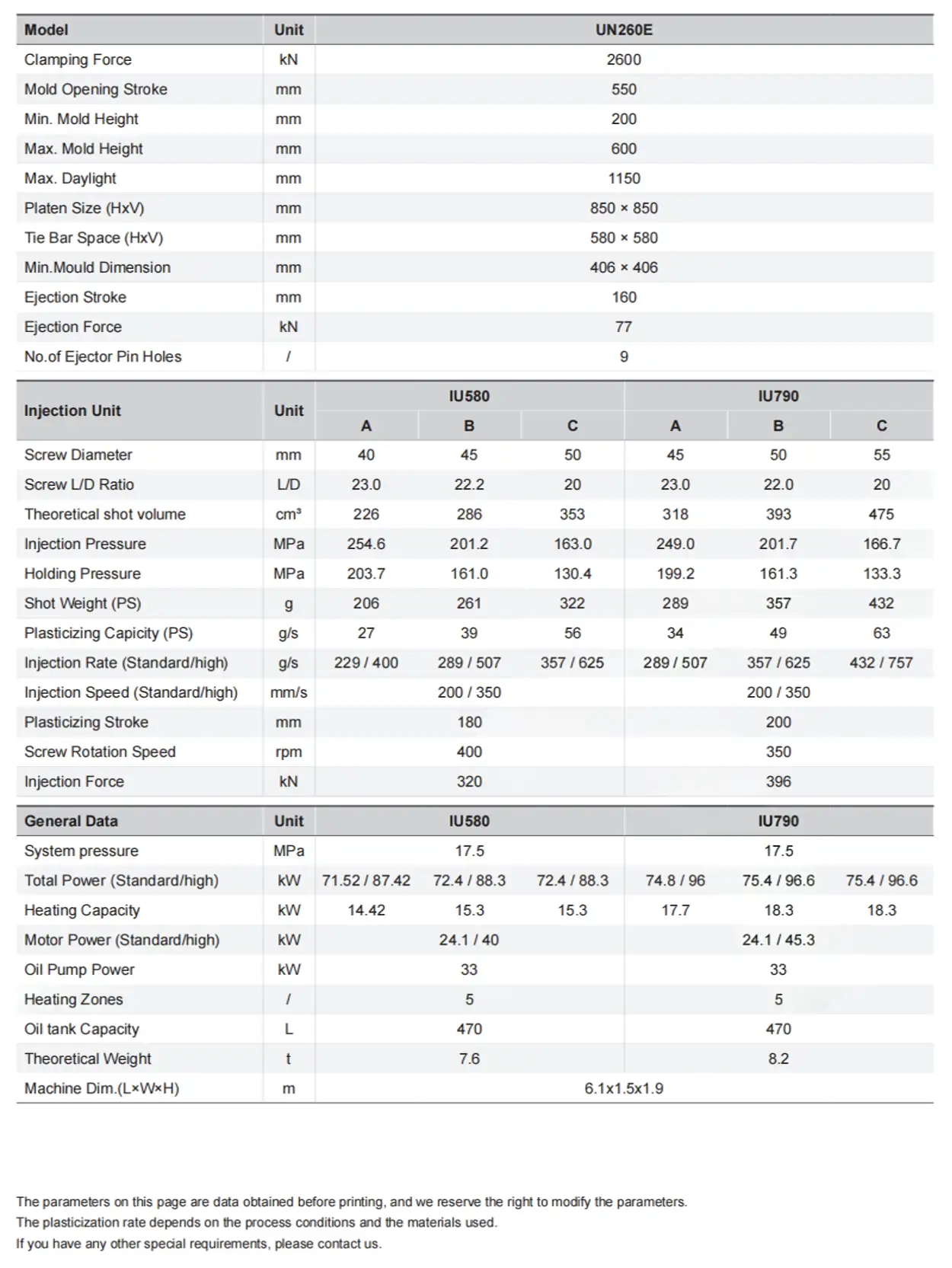
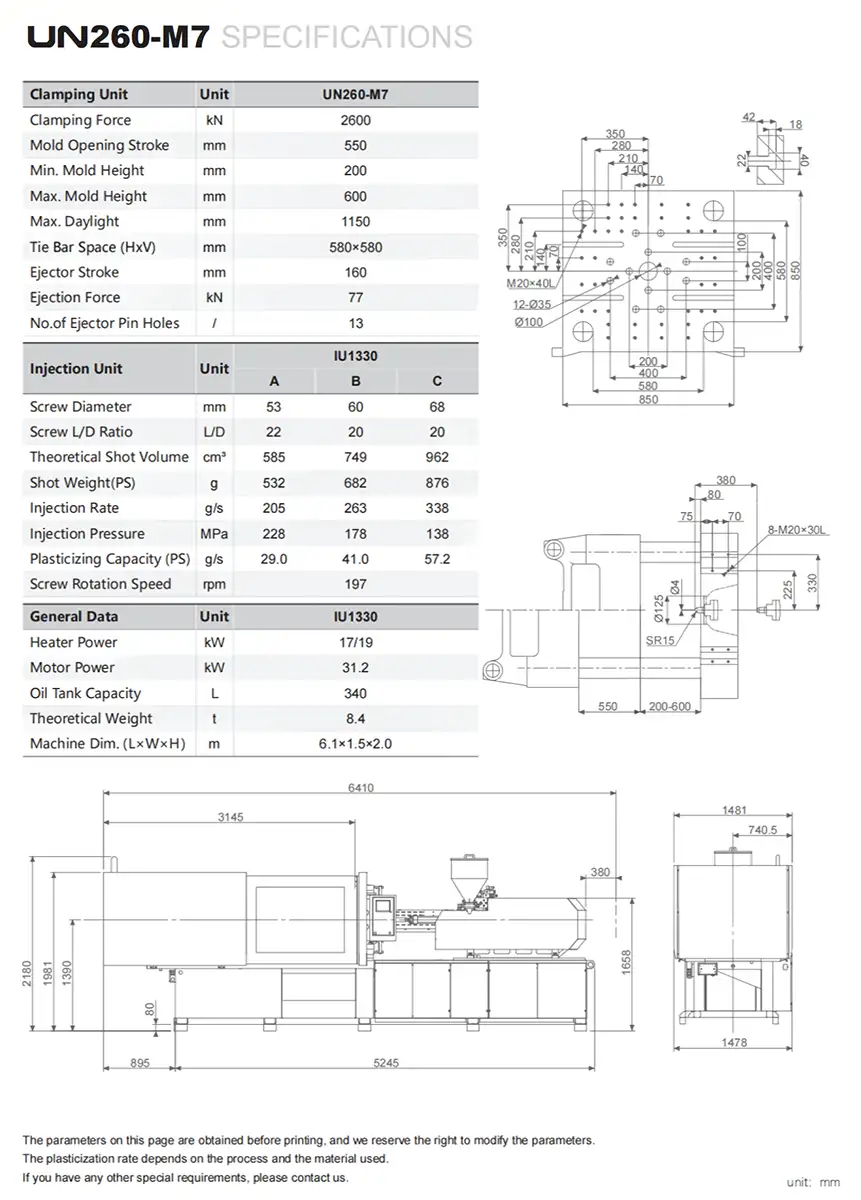
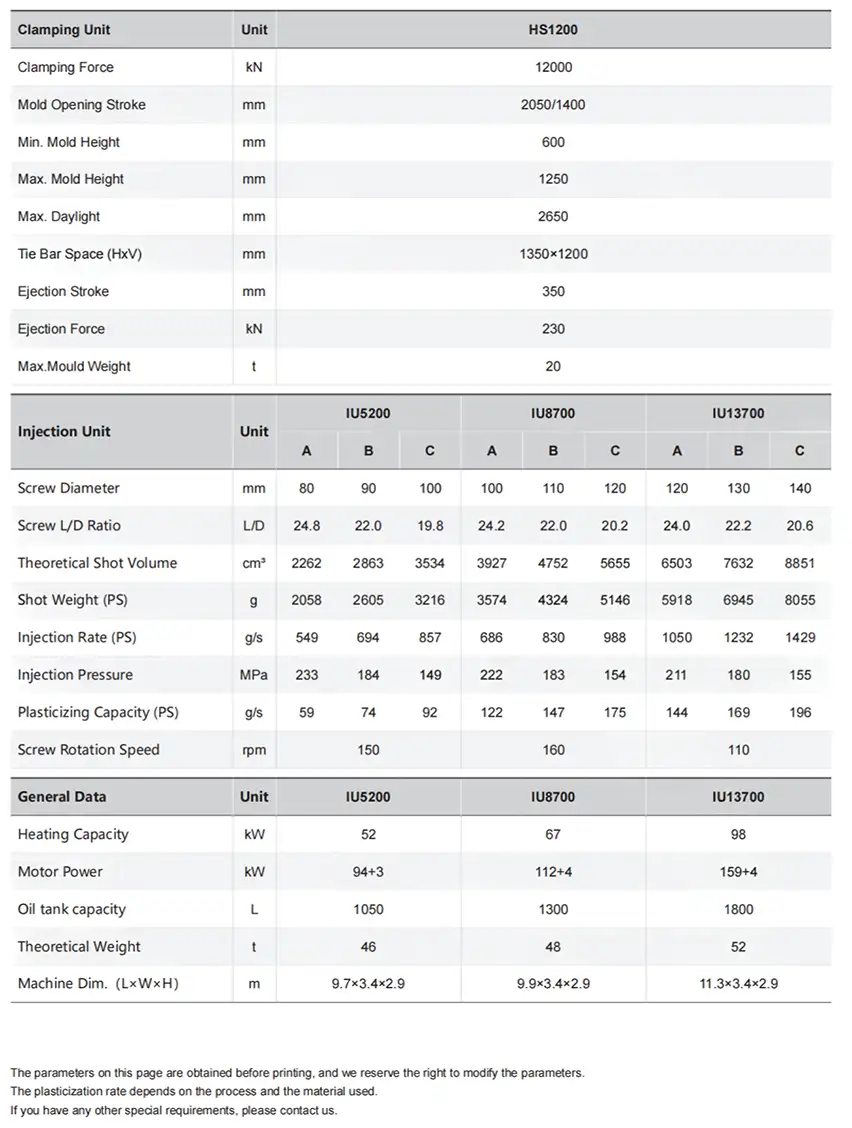
| Clamping Unit | Unit | ES120 | |||||
| Clamping Force | kN | 1,200 | |||||
| Mold Opening Stroke | mm | 360 | |||||
| Min. Mold Height | mm | 180 | |||||
| Max. Mold Height | mm | 450 | |||||
| Max. Daylight | mm | 810 | |||||
| Platen Size (HxV) | mm | 670 × 620 | |||||
| Tie Bar Space (HxV) | mm | 470 × 420 | |||||
| Min.Mould Dimension | mm | 305 × 270 | |||||
| Max.Mould Weight | t | 1 | |||||
| Ejection Stroke | mm | 110 | |||||
| Ejection Force | kN | 40 | |||||
| No.of Ejector Pin Holes | / | 5 | |||||
| Injection Unit | Unit | IU180 | IU260 | ||||
| A | B | C | A | B | C | ||
| Screw Diameter | mm | 26 | 30 | 34 | 30 | 34 | 38 |
| Screw L/D Ratio | L/D | 23 | 23 | 20 | 23 | 22.4 | 20 |
| Theoretical Shot Volume | cm³ | 64 | 85 | 109 | 99 | 127 | 159 |
| Injection Pressure | MPa | 283 | 212 | 165 | 272 | 212 | 169 |
| Holding Pressusre | MPa | 226 | 170 | 132 | 217 | 169 | 136 |
| Shot Weight (PS) | g | 58 | 77 | 99 | 90 | 116 | 144 |
| Plasticizing Capacity (PS) | g/s | 10 | 13 | 16 | 13 | 18 | 23 |
| Injection Rate (Standard/High) | g/s | 97 / 217 | 129 / 289 | 165 / 372 | 129 / 289 | 165 / 372 | 206 / 464 |
| Injection Speed (Standard/High) | mm/s | 200 / 450 | 200 / 450 | ||||
| Plasticizing Stroke | mm | 120 | 140 | ||||
| Screw Rotation Speed | rpm | 400 | 400 | ||||
| Nozzle Contact Force | kN | 25 | 25 | ||||
| General Data | Unit | IU180 | IU260 | ||||
| Total Power (Standard/High) | kW | 17.0 / 30.6 | 18.3 / 31.9 | 18.3 / 31.9 | 23.5 / 39.2 | 25.7 / 41.4 | 25.7 / 41.4 |
| Heating Capacity | kW | 6.50 | 7.80 | 7.80 | 7.80 | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| Motor Power (Standard/High) | kW | 10.5 / 24.1 | 15.7 / 31.4 | ||||
| Heating Zones | / | 5.00 | 5.00 | ||||
| Theoretical Weight | t | 5.80 | 5.90 | ||||
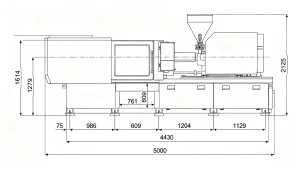
| Machine Dim.( L×W×H) | m | 5.0×1.4×1.7 | |||||
Performance Profile
Core Capabilities
120-ton machines are optimized for medium-sized, highly detailed parts, ensuring high repeatability and minimal material waste.
- Part Sizing: Effective projected area management up to 350 cm² (approximately 54 in²) to maintain mold integrity during peak injection.
- Material Versatility: The standard 20:1 L/D ratio supports efficient plasticizing of commodity resins (e.g., PP, PE, PS) and engineering thermoplastics (e.g., ABS, PC, Nylon).
- Production Volume: Capable of running multi-cavity molds (typically 2 to 8 cavities) for small components.
- Speed Metric: Dry cycle times (clamp open to close) routinely achieve 2.0 seconds or less, enabling optimized molding cycles.
Limitations
Constraints must be factored into part design, particularly concerning volume and physical size.
- Maximum Shot Weight Constraint: The theoretical shot volume restricts finished part weight, typically below 250 grams for thick-walled components.
- Dimensional Constraint: Mold base size is strictly limited by the Tie Bar Clearance (470 x 420 mm Nominal), which prohibits large-format toolsets.
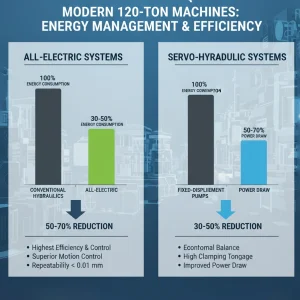
Energy Efficiency and Precision
Modern 120-ton machines prioritize energy management, with the adoption of specialized drive systems being the industry norm:
- All-Electric Systems: Offer the highest level of efficiency and control. Energy consumption is typically reduced by 50% to 70% compared to conventional hydraulics. They provide superior motion control for the most demanding parts, achieving repeatability below 0.01 mm.
- Servo-Hydraulic Systems: Provide a more economical balance, reducing power draw by 30% to 50% versus older fixed-displacement pumps while maintaining high clamping tonnage output.
These energy-saving technologies directly enhance the economic viability of the operation and ensure the sustained, long-term value of the equipment.
Need Detailed Technical Specifications?
Our engineering team can provide customized specifications based on your production requirements. Request a technical datasheet with performance metrics specific to your application.
Key Advantages of 120-Ton Injection Molding Machines
The 120-ton injection molding machine class presents distinct technical and operational advantages, positioning it as the preferred equipment for manufacturers requiring balanced performance, resource optimization, and high product diversity in mid-volume environments.
Operational Versatility and Adaptability

The 120-ton capacity is the optimal nexus for production versatility, proficiently handling a broad spectrum of technical requirements.
- Part and Tooling Range: The machine comfortably manages multi-cavity tools for smaller parts while still accommodating medium-sized components up to its 350 cm² projected area limit.
- Material Flexibility: Its standard plasticizing unit is configured to process common commodity resins (PP, PE) as well as demanding engineering thermoplastics (PC, PEEK), minimizing the need for specialized equipment changes.
- Production Agility: The mid-range size facilitates faster mold changeovers and shorter setup times than larger machinery, supporting efficient manufacturing of diverse Stock Keeping Units (SKUs).
Cost-Effectiveness
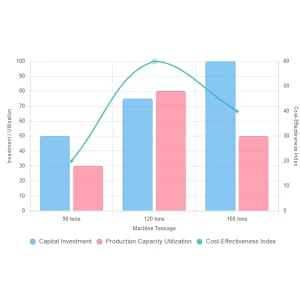
This machine segment provides a maximized utilization of capital resources relative to production output.
- Capacity Alignment: The 120-ton class delivers substantial production capability necessary for medium-volume runs, effectively minimizing capital overhead that would be required for acquiring underutilized, higher-tonnage equipment.
- Sustained Throughput: It ensures consistent, high-rate throughput for the majority of precision parts without over-investing in unused clamping force, directly supporting long-term production stability.
Space Efficiency
Efficient use of production floor space is a defining advantage of the 120-ton class.
- Space Consolidation: With typical operational dimensions around 5.0 × 1.4 × 1.7 meters, the machine provides a substantial tonnage-per-square-meter ratio, allowing
- Layout Flexibility: The compact operational footprint simplifies factory floor planning, enabling more flexible and efficient cell manufacturing layouts.
Precision and Power Efficiency
Leveraging modern drive technologies, the 120-ton machine enhances part quality and operational metrics.
- Enhanced Repeatability: The prevalence of all-electric and servo-hydraulic systems in this class ensures superior motion control, directly translating to dimensional repeatability below 0.01 mm—critical for automotive and medical parts.
- Optimized Power Draw: The installed power (typically 11–16 kW during operation) is directly managed by servo technology, ensuring that power is consumed proportional to the force demanded, rather than continuously, maximizing long-term operational sustainability.
Selection Criteria and Applications
Selecting the right injection molding machine requires careful consideration of multiple factors. Professionals evaluating 120-ton machines must follow a structured technical evaluation to ensure the machine’s constraints are optimally aligned with production requirements.
Key Factors for Selection
Production Requirements
- Part projected area and volume; Required material viscosity and melt temperature.
- Cycle time targets and cooling demands.
- Dimensional tolerance and surface finish specifications.
- Directly determines necessary Clamping Force (tonnage) and Shot Volume.
- Influences the choice between all-electric (speed) and servo-hydraulic systems.
- Dictates the required machine Repeatability (e.g., all-electric systems for <0.01 mm precision).
Physical Constraints
- Machine footprint and Tonnage-to-Area Ratio.
- Platen dimensions and Tie Bar Clearance.
- Minimum/Maximum Mold Shut Height.
- Essential for plant layout planning and space utilization.
- Determines the maximum physical size of the mold base.
- Ensures the mold tool fits securely between the platen surfaces.
Operational Efficiency Metrics
- Power consumption (kW) and energy source type (Servo vs. All-Electric).
- Labor complexity and automation integration requirements.
- Planned maintenance schedule and spare parts logistics.
- Impacts long-term utility usage and operational sustainability.
- Affects staffing models and auxiliary equipment placement.
- Determines equipment uptime predictability.
Suitable Industries and Applications
The 120-ton machine excels in applications demanding precision in mid-sized components and high-cavitation runs for smaller parts, making it a critical asset across several high-specification industries:
Automotive Sub-Assemblies
- Medium-sized, highly cosmetic interior trim components.
- Electrical connector housings.
- Non-structural under-the-hood fasteners and brackets.
Electronics Enclosures
- Precision device housings and structural chassis components.
- Intricate switch and terminal block assemblies requiring tight dimensional tolerances.
Medical and Laboratory Consumables
- High-volume sample containers and diagnostic equipment casings.
- Detailed non-implantable device components that demand high material purity and repeatability.
Specialty Packaging
- Multi-cavity tools for high-volume thin-walled caps and closures.
- Medium-sized food storage containers requiring precise sealing surfaces.

Comparison with Other Tonnage Machines
Understanding how 120-ton machines compare to lower and higher tonnage alternatives helps manufacturers select the optimal equipment for their specific requirements.
| Specification | 80-100 Ton Machines | 120 Ton Machines | 150-200 Ton Machines |
| Typical Projected Area Max | Small (up to 155 cm² / 24 in²) | Medium (up to 350 cm² / 54 in²) | Medium-Large (up to 600 cm² / 93 in²) |
| Shot Volume Range (Theoretical) | 100 – 150 cm³ | 163 – 265 cm³ | 300 – 450 cm³ |
| Platen Size (Nominal) | 500 × 450 mm | 610 × 560 mm | 750 × 700 mm |
| Floor Space (Approximate) | 8-10 m² | 10-12 m² | 15-20 m² |
| Energy Consumption (Operating) | 8-12 kW | 11-16 kW | 18-25 kW |
| Typical Part Weight Max | Under 150 grams | Under 250 grams | Under 400 grams |
| Typical Applications | Precision electrical connectors, small vials/caps, medical luer fittings, small gear components. | Automotive interior trim, electronic device enclosures, multi-cavity closures, medical diagnostic components. | Mid-size housing/panels, large kitchenware (bowls), automotive instrument panels (small), thicker-walled containers. |
Need Help Comparing Different Tonnage Options?
Our equipment specialists can help you evaluate which machine tonnage best suits your specific production requirements. Request a personalized comparison analysis.
Future Trends and Technological Advancements
The injection molding industry continues to evolve with technological innovations that enhance the capabilities and efficiency of 120-ton machines. Understanding these trends helps manufacturers make forward-looking equipment decisions.
Sustainable Power Systems and Efficiency
Next-generation 120 ton machines are defined by their commitment to energy optimization and environmental responsibility.
- All-Electric Dominance: The transition to dedicated all-electric systems, replacing conventional hydraulics, allows for energy consumption reductions of up to 70\%. This improvement stems from using power only when motion is required and implementing energy recovery during deceleration phases.
- Precision Driving: High-response servo-electric axes provide highly precise motion control for injection and clamping, directly enhancing part quality and minimizing energy waste associated with inefficient motion profiles.
Industry 4.0 and Production Digitization
Integration capabilities are transforming the 120 ton machine from a standalone unit into a networked asset, enabling sophisticated factory management.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Enhanced connectivity, often utilizing IoT sensors and standardized communication protocols (such as OPC UA), facilitates continuous, real-time data streaming from the machine to central Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES).
- Predictive Maintenance: Data analytics applied to operational parameters (e.g., motor temperatures, valve actuation counts) enable predictive maintenance algorithms. This proactively schedules service interventions based on actual wear, significantly maximizing equipment uptime and extending component life.
- Digital Twin Capability: The captured operational data supports the creation of a Digital Twin, allowing engineers to simulate process changes and optimize production settings virtually before applying them to the physical machine.
Adaptive Process Control
The introduction of intelligent control platforms represents the next leap in maintaining ultra-high quality and process resilience, regardless of external disturbances.
- Self-Correction: Sophisticated control systems integrate AI and machine learning to enable adaptive process control. The machine automatically adjusts key parameters (e.g., hold pressure, pack time) to counteract variations in material viscosity, ambient temperature, or melt consistency.
- Tolerance Stability: This self-adjusting capability is critical for maintaining extremely tight tolerances, ensuring that high-precision parts, often requiring dimensional repeatability below ± 0.01 mm, are consistently produced even under dynamic manufacturing conditions.
- User Interface Evolution: Control systems are moving toward intuitive, graphics-based interfaces that provide operators with deep process visibility and diagnostic guidance, simplifying complex parameter management.
Conclusion
The 120-ton injection molding machine represents an optimal balance of capabilities for medium-scale manufacturing operations. Its specific clamping force and injection capacity establish a versatile and powerful platform for medium-volume, high-precision component manufacturing.
For professionals evaluating equipment, the core principle remains technical matching: ensuring the projected area and material characteristics are precisely aligned with the machine’s capacity. The 120 ton class offers a robust operating envelope that maintains production efficiency and component quality across diverse application requirements.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced technologies—specifically all-electric motion control and Industry 4.0 connectivity—will continuously expand the operational boundaries of this machine size. By embracing these advancements, the 120 ton machine secures its long-term viability as a reliable, high-throughput asset for future-oriented production facilities.