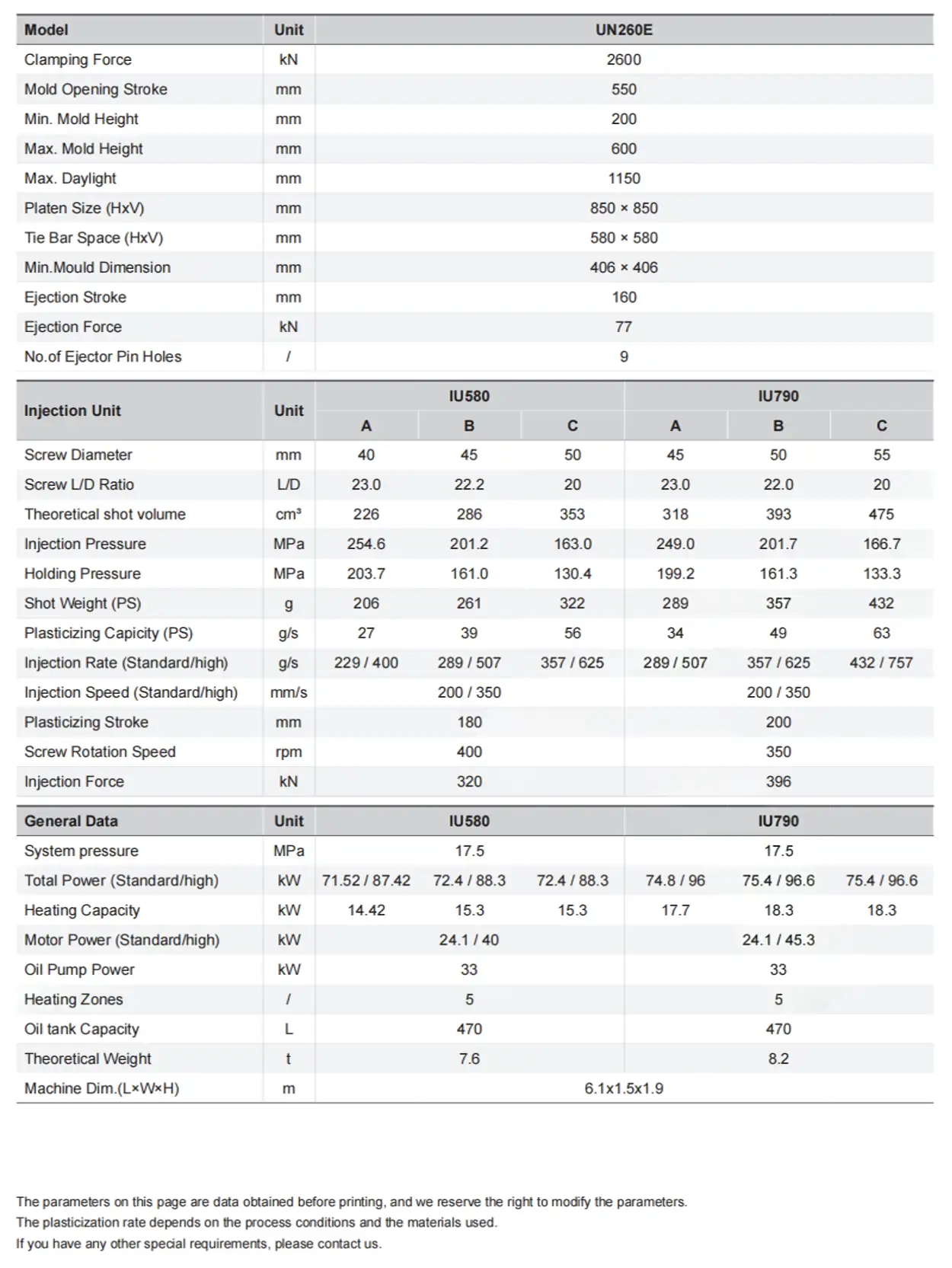
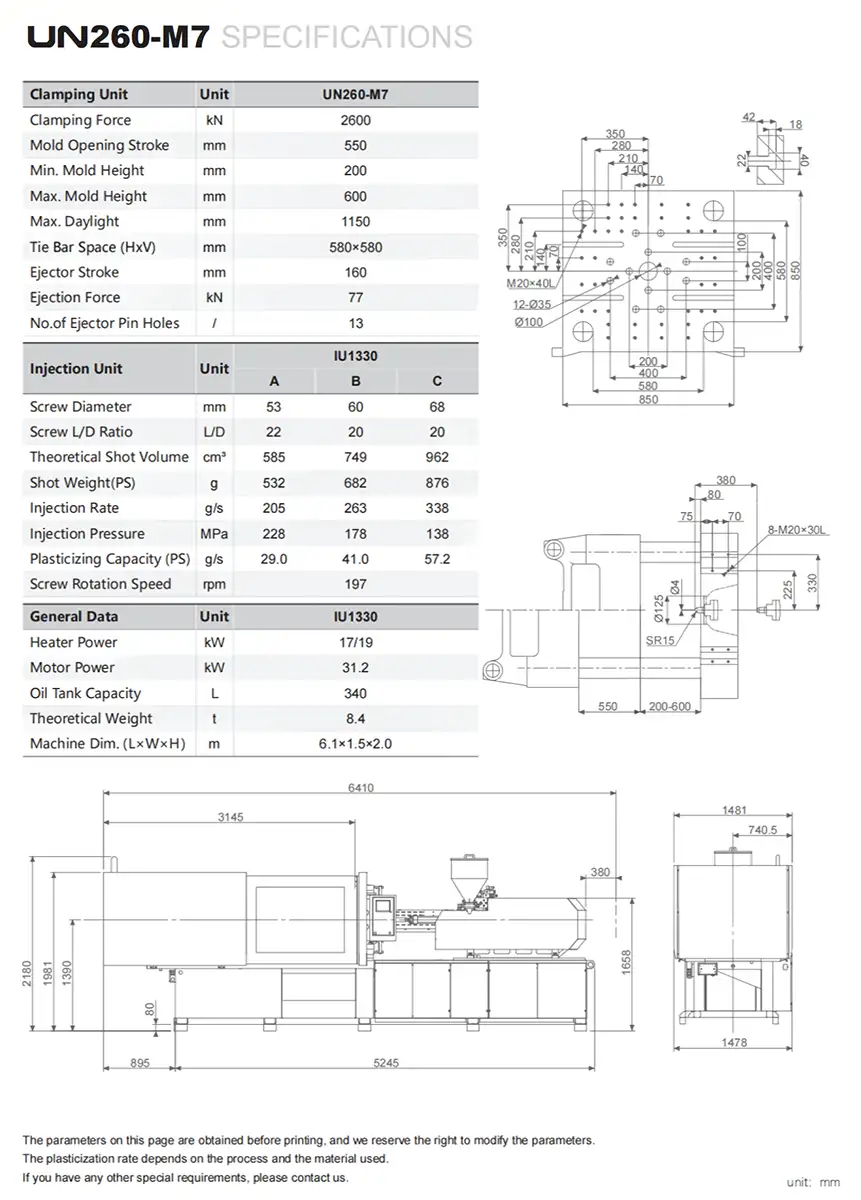
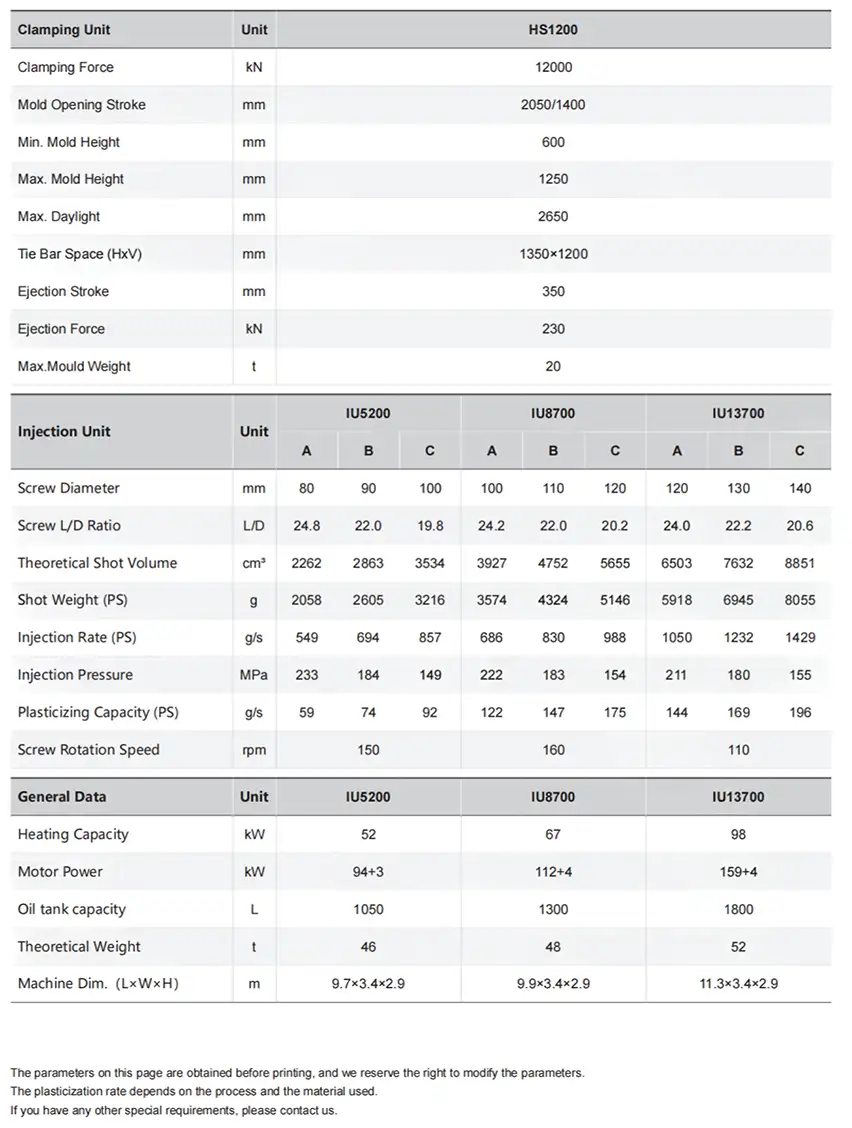
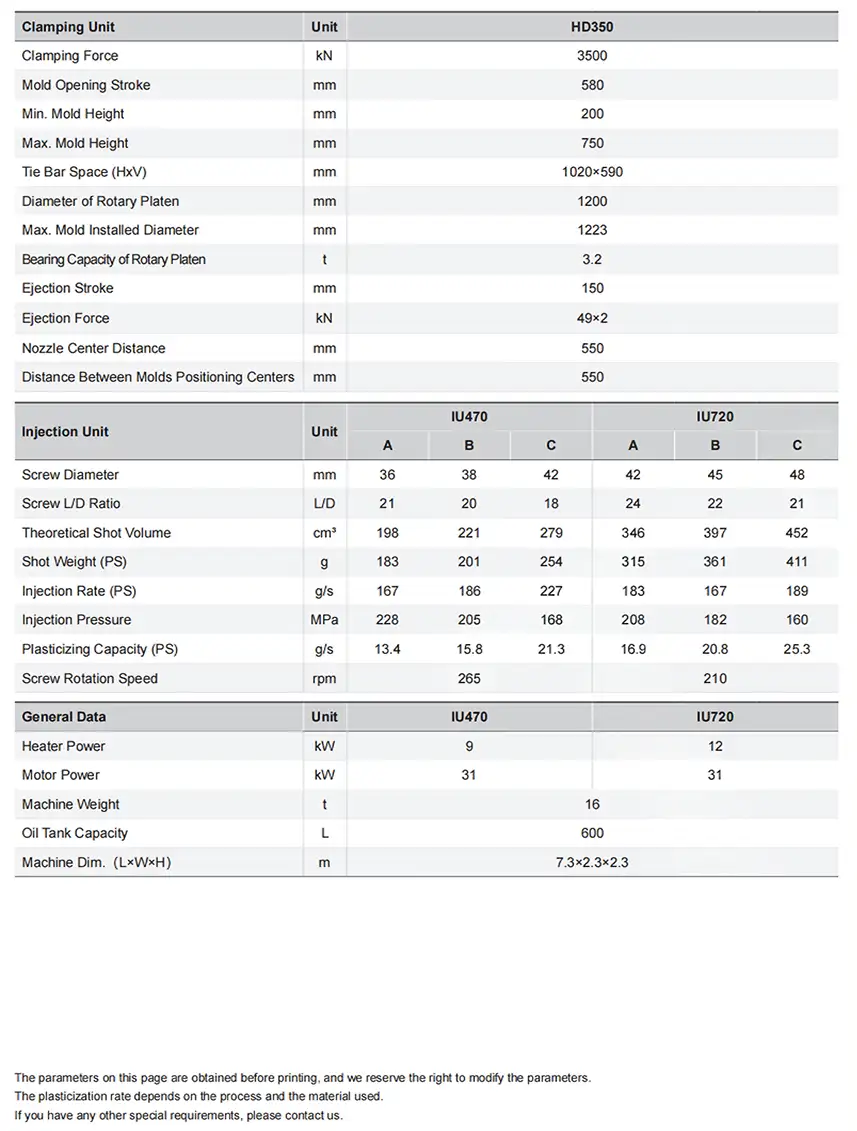
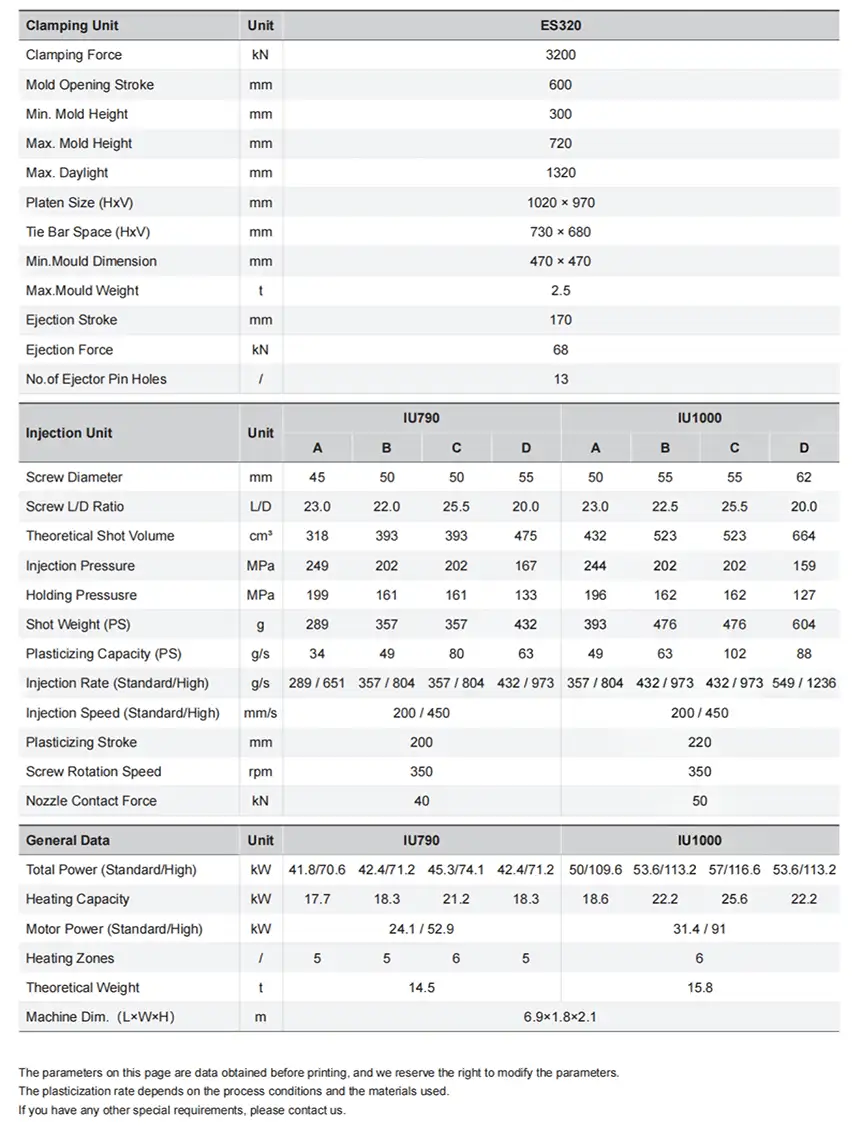
Hydraulic injection molding machines are a cornerstone of modern plastic manufacturing, powering the production of countless parts, from intricate medical devices to robust automotive components. These workhorse machines are valued by production managers and engineers for their exceptional clamping force and injection control, capabilities derived from their sophisticated hydraulic systems. They excel in demanding production environments, delivering a consistent performance that is crucial for maintaining product quality and operational efficiency. By exploring the core functionalities, advantages, and application specificities of hydraulic machines, these professionals can make informed decisions to enhance their production capabilities.
What is a Hydraulic Injection Molding Machine?
A hydraulic injection molding machine is a powerful system that leverages hydraulic pressure to shape molten plastic into finished parts. It’s the workhorse of high-volume manufacturing, taking raw plastic pellets and transforming them into complex products with repeatable precision. The machine’s core power lies in its ability to generate and control massive forces for both molding and ejection. These machines are engineered around three primary components that work in a synchronized molding cycle:
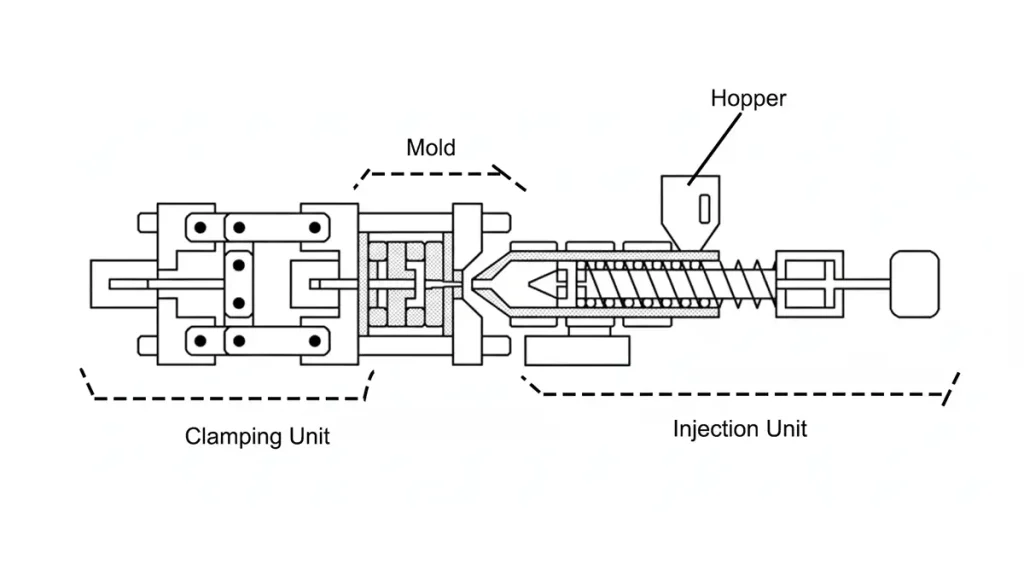
- Clamping Unit: This unit secures the mold during injection and applies a precise closing force to prevent the mold from opening under pressure.
- Injection Unit: This component is responsible for melting and injecting the plastic resin into the mold cavity.
- Hydraulic System: The powerhouse of the machine, it uses a pump and cylinders to generate and control the immense forces required for clamping and injection.
The core principle lies in the application of high-pressure hydraulic oil, which is precisely directed to various actuators to achieve consistent movement and force. This mechanism is particularly effective for molding large, thick-walled, or complex parts that demand sustained high pressure.
Hydraulic vs. Other Technologies
| Hydraulic Strengths | Hybrid Solutions |
|---|---|
| High Clamping Force: Ideal for large parts requiring high tonnage (>500 tons). | Electric motors for high-speed, precise movements like screw rotation and part ejection. |
| Cost-Effectiveness: Lower initial investment for high-force applications. | Hydraulic pumps for high-force tasks such as clamping and injection. |
| Durability and Stability: Robust design absorbs shock for complex molds. | Servo-controlled hydraulic pumps that only activate when needed, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to traditional hydraulic systems. |
This integrated approach delivers the force of a hydraulic system with the energy efficiency and control of an electric one, offering a versatile solution for a wide range of molding applications.
Key Characteristics & Considerations
As the industry’s workhorse, hydraulic injection molding machines have a well-defined set of capabilities that make them a preferred solution for certain applications. Their robust design and sheer power are more than just technical specifications; they translate directly into tangible production benefits. To make an informed choice, it’s essential to look beyond the initial investment and understand how these machines’ core strengths—and their limitations—impact operational efficiency, product quality, and long-term costs.
Core Strengths
- Powerful Clamping Force: Hydraulic systems are engineered to generate immense clamping forces, from 50 to over 4,000 tons. This capability is essential for producing large parts and thick-walled components that demand sustained pressure.
- Robust Pressure Control: Thanks to advanced hydraulic circuits, these machines provide precise pressure regulation throughout the injection and holding phases, ensuring consistent part quality and dimensional stability.
- Durability: Built with heavy-duty components, hydraulic machines are designed for continuous, high-duty cycles. Their robust construction and excellent shock absorption protect both the machine and the mold, extending their lifespan.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For high-tonnage applications (typically over 500 tons), hydraulic machines present a lower initial capital investment compared to all-electric alternatives.
- Versatility: They excel at processing a wide range of materials, including standard and engineering-grade polymers that require high injection pressures.
Limitations
- Energy Consumption: While modern servo-hydraulic systems have improved, traditional hydraulic machines still consume more energy during idle phases compared to electric models.
- Noise and Fluid Management: Hydraulic systems are inherently louder than electric ones, and the potential for fluid leaks requires regular maintenance and a clean operating environment.
- Precision: For applications requiring extremely high precision or the molding of ultra-thin-walled parts, all-electric machines often provide superior repeatability.
- Environmental Factors: The use of hydraulic oil and the need for cooling systems are important considerations, especially in cleanroom or temperature-sensitive environments.
Classification of Injection Molding Machines Based on Injection Unit Arrangement
Hydraulic injection molding machines are configured in different layouts, each designed to optimize specific production workflows and part types. The arrangement of the injection and clamping units is a fundamental consideration that determines the machine’s primary application.
Here is a breakdown of the primary configurations:
Horizontal (Standard) Machines
This is the most common and versatile configuration, with the injection and clamping units aligned on a single horizontal axis.
- Key Advantages: Their open layout simplifies part removal, enabling efficient gravity-drop or robotic automation. This makes them ideal for high-volume production of a wide range of parts.
- Primary Use: Best suited for general-purpose molding, producing medium to large parts with complex geometries.
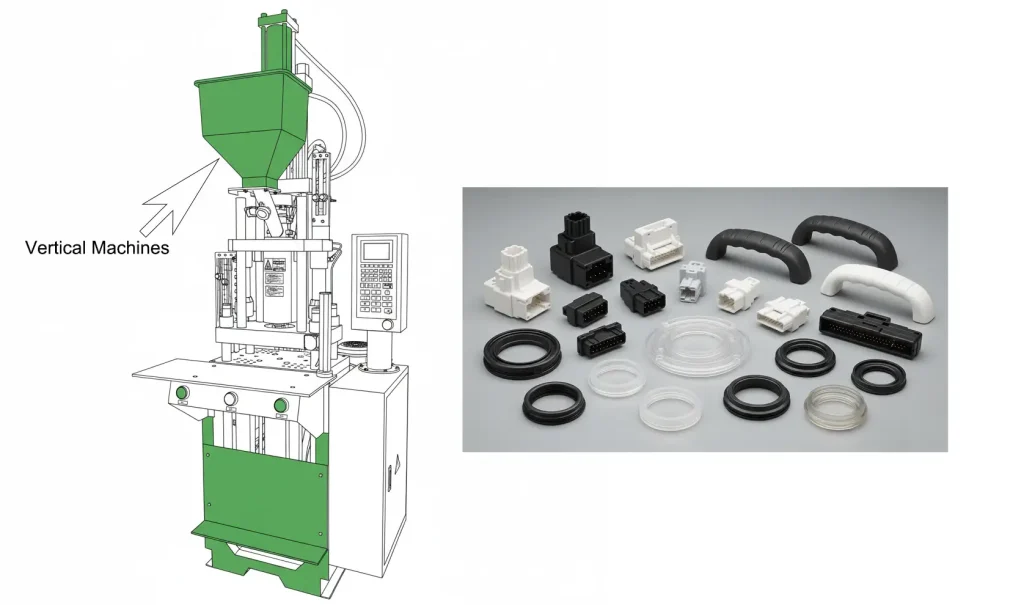
Vertical Machines
Vertical machines are built with the clamping unit on a horizontal plane and the injection unit positioned perpendicularly on top. This unique design is tailored for specialized applications.
- Key Advantages: The vertical layout is perfect for insert molding and overmolding, providing easy access for operators to manually place components. It also offers a significantly smaller footprint, saving valuable floor space.
- Primary Use: Common in the electronics and medical industries for parts requiring integrated components, such as connectors, handles, and seals.
Multi-Component Machines
These specialized machines incorporate multiple injection units to mold parts from different materials or colors in a single cycle, eliminating the need for secondary assembly.
- Key Advantages: Provides the ability to produce complex parts with multiple materials, such as soft-touch grips on a hard plastic part, or multi-color components.
- Primary Use: Essential for industries producing consumer goods, automotive parts, and medical devices that require multi-material functionality or aesthetics. These machines are available in various layouts, including rotary platen systems and piggyback units, to accommodate a wide range of part designs.
The Function of the Hydraulic System in Injection Molding Machines
The hydraulic system is the backbone of an injection molding machine, translating mechanical power into the immense force and precise motion required for molding. It is a closed-loop circuit of pumps, valves, and cylinders that together control every phase of the molding cycle.
| Component | Function | Impact on Performance |
| Hydraulic Pump | Converts mechanical power into hydraulic pressure. | Determines the system’s maximum pressure and flow rate, directly affecting injection speed and clamping force. |
| Control Valves | Regulate flow direction, rate, and pressure. | Provide precise control over injection speed, pressure profiling, and the sequencing of all operations. |
| Hydraulic Cylinders | Convert hydraulic pressure into linear motion. | The primary actuators for generating clamping force and moving the injection screw. |
| Accumulators | Store hydraulic energy to meet peak demand. | Stabilize system pressure, reduce pump size, and accelerate high-speed movements. |
Hydraulic Functions in the Molding Cycle
The hydraulic system orchestrates the entire molding process, from securing the mold to ejecting the final part.
Clamping
Injection
Auxiliary Operations
- Applies immense force to keep mold halves closed.
- Controls slow, precise mold opening and closing.
- Prevents mold separation during high-pressure injection.
- Drives the screw forward to inject molten plastic.
- Controls speed and pressure during filling and packing.
- Ensures a dense, defect-free part.
- Powers core pulls and slides for complex molds.
- Activates ejector pins for part removal.
- Regulates nozzle contact force.
Enhancements for Efficiency
Modern hydraulic machines integrate advanced technologies to significantly improve energy efficiency and performance.
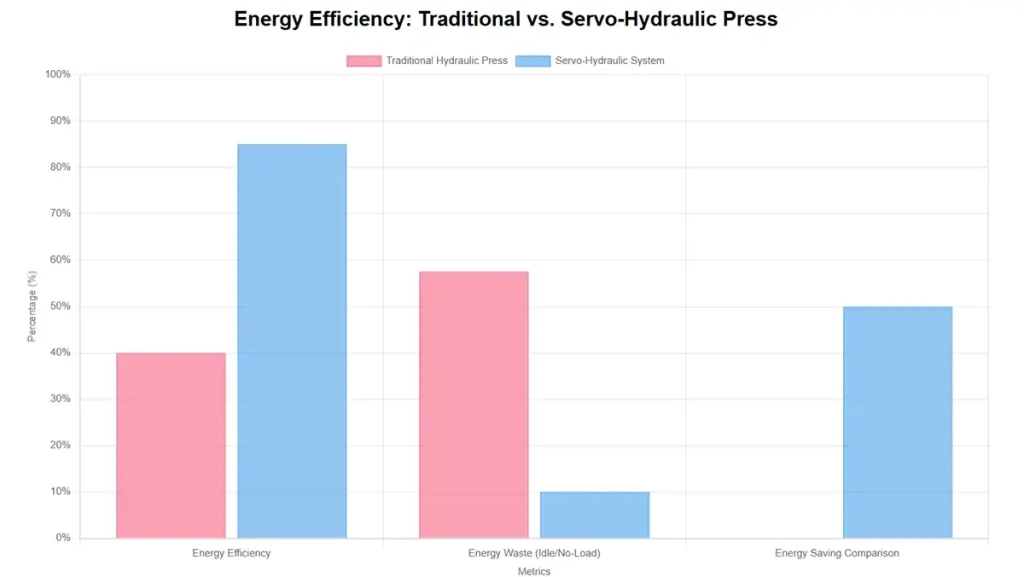
- Servo-Hydraulic Systems: These systems use servo motors to drive hydraulic pumps only when required by the machine, eliminating energy waste during idle periods. This can lead to energy savings of up to 70% compared to conventional systems.
- Variable Displacement Pumps: These pumps automatically adjust their output flow based on the real-time needs of the system, reducing energy consumption during low-flow phases.
- Intelligent Pressure Control: Advanced control systems maintain only the precise pressure needed for each stage of the process, avoiding excessive power usage.
Recommendations for Hydraulic Injection Molding Machine Manufacturers
Choosing a hydraulic injection molding machine isn’t just about technical specifications—it’s about selecting a long-term partner who will support your production goals. A thorough evaluation of a manufacturer’s capabilities, support, and business practices is essential for ensuring a successful and profitable investment.
Key Evaluation Criteria
1. Technical Capabilities & Quality Look for a supplier with proven expertise in manufacturing precision and robust quality control. Their technical strength is reflected in the machine’s durability, molding repeatability, and ability to be integrated with modern automation and Industry 4.0 systems.
2. Service & Support Effective after-sales support is critical for maximizing machine uptime. A reliable manufacturer offers:
- Local Technical Support: Accessible and timely on-site or remote assistance.
- Spare Parts Availability: A well-stocked local or regional inventory to minimize downtime.
- Operator Training: Comprehensive programs to ensure your team can operate and maintain the machine effectively.
3. Business & Financial Stability Assess a manufacturer’s market reputation and financial health. This ensures they can provide long-term support and honor warranty commitments. Consider seeking references from existing customers to gauge their satisfaction and long-term viability.
Considering the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The initial purchase price is only part of the investment. A total cost of ownership analysis should also factor in:
- Energy Consumption: Look for machines with servo-hydraulic systems, which can significantly reduce energy use.
- Maintenance & Service Costs: Evaluate the cost of spare parts, hydraulic fluid, and regular service.
- Potential Downtime: The quality of service and support directly impacts operational uptime and profitability.
Compare Machine Specifications
Request detailed specifications from multiple manufacturers to find the perfect match for your production requirements.
Certifications and Standards
Reputable manufacturers will hold key industry certifications that demonstrate their commitment to quality, safety, and environmental responsibility.
- ISO 9001: Certifies a quality management system.
- CE Marking & UL/CSA: Ensures compliance with strict European and North American safety standards.
- Euromap & OPC UA: Demonstrates adherence to industry communication protocols, enabling seamless integration into automated production lines.

Conclusion
Hydraulic injection molding machines remain a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, not merely as a legacy technology, but as a specialized and indispensable solution. Their core strengths—the ability to generate immense clamping force, handle complex molds with ease, and offer a cost-effective solution for large-part production—solidify their position in the industry.
While all-electric machines have pushed the boundaries of speed and efficiency, the hydraulic system’s durability and raw power are unparalleled in high-tonnage applications. This makes them a vital investment for industries where strength and reliability are paramount.
Looking ahead, the future of injection molding is not defined by a single technology but by a fusion of capabilities. The rise of hybrid systems, which combine the force of hydraulics with the precision and energy savings of electric drives, is a testament to the continued evolution of this technology. These innovations ensure that the fundamental principles of hydraulic molding will remain a powerful and competitive force in the manufacturing landscape for years to come.
Ready to Find Your Ideal Hydraulic Injection Molding Machine?
Our team of experts can help you evaluate your production requirements and connect you with qualified manufacturers offering the best solutions for your specific needs.