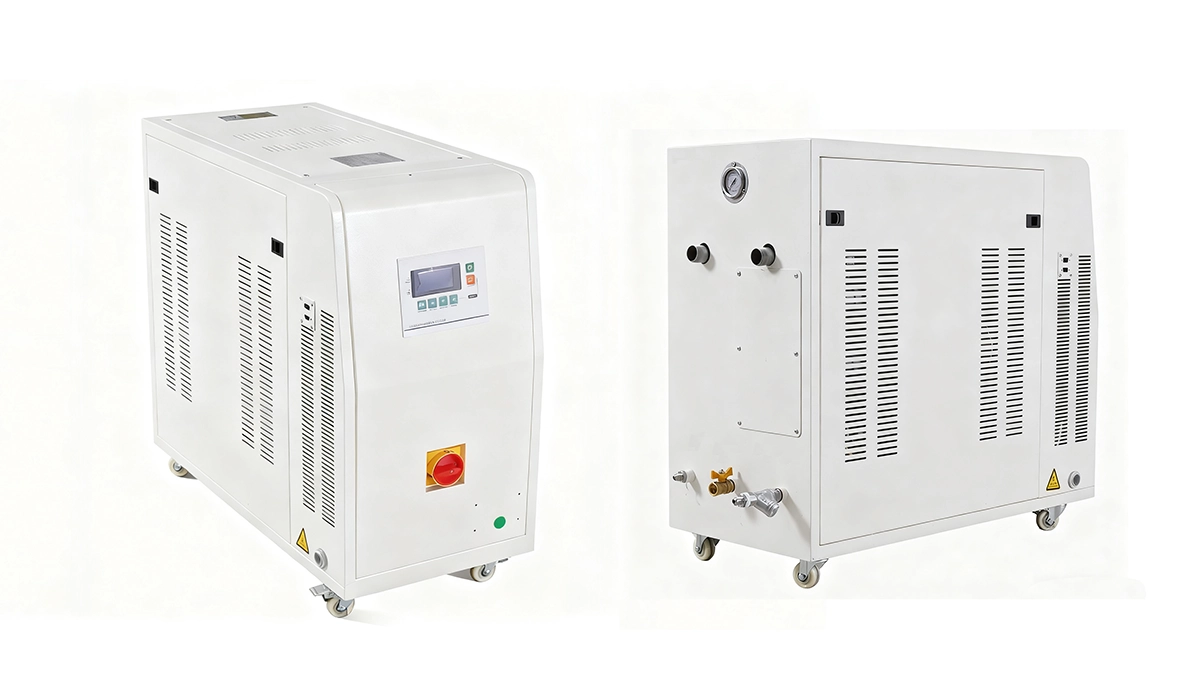
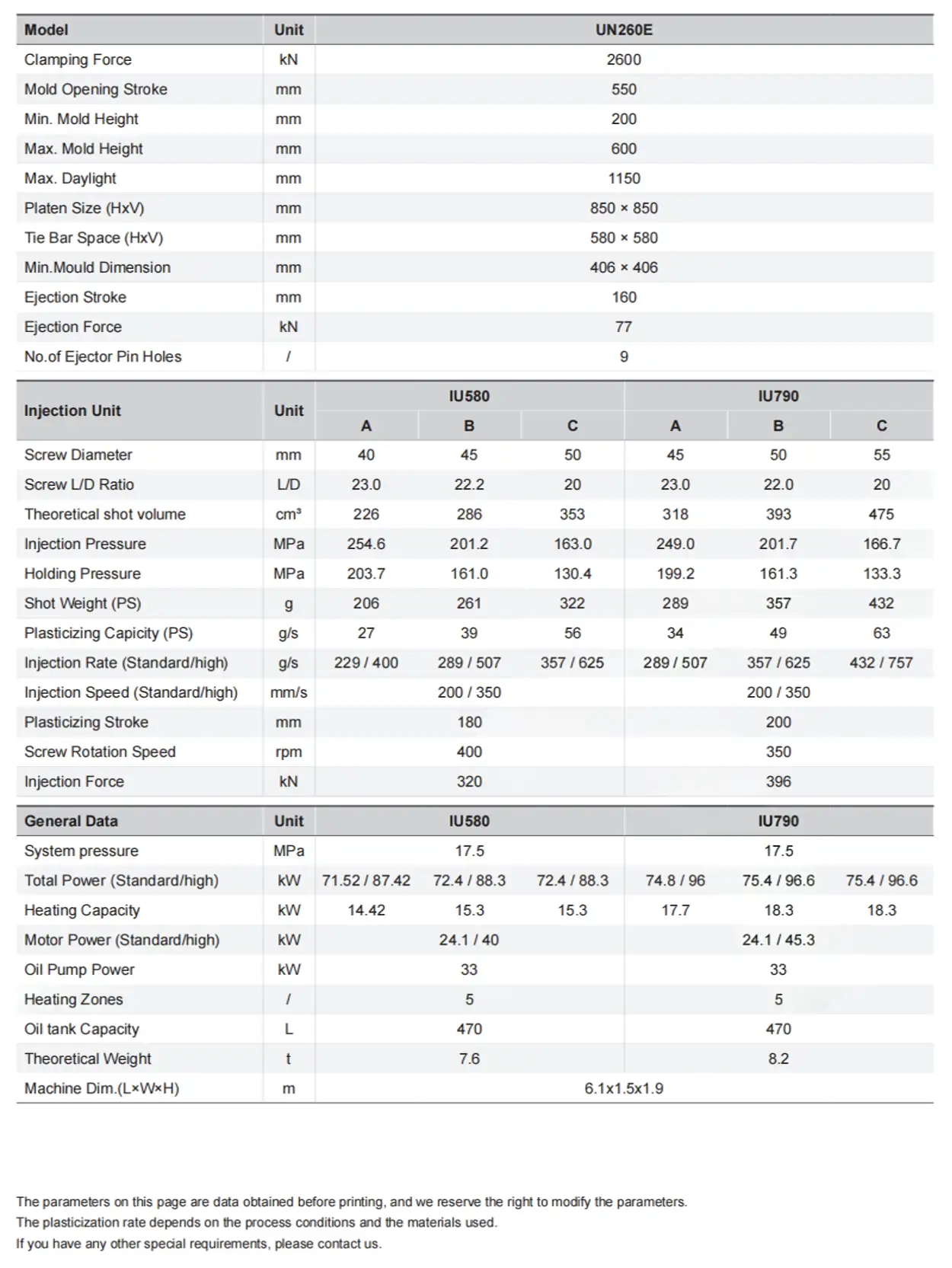
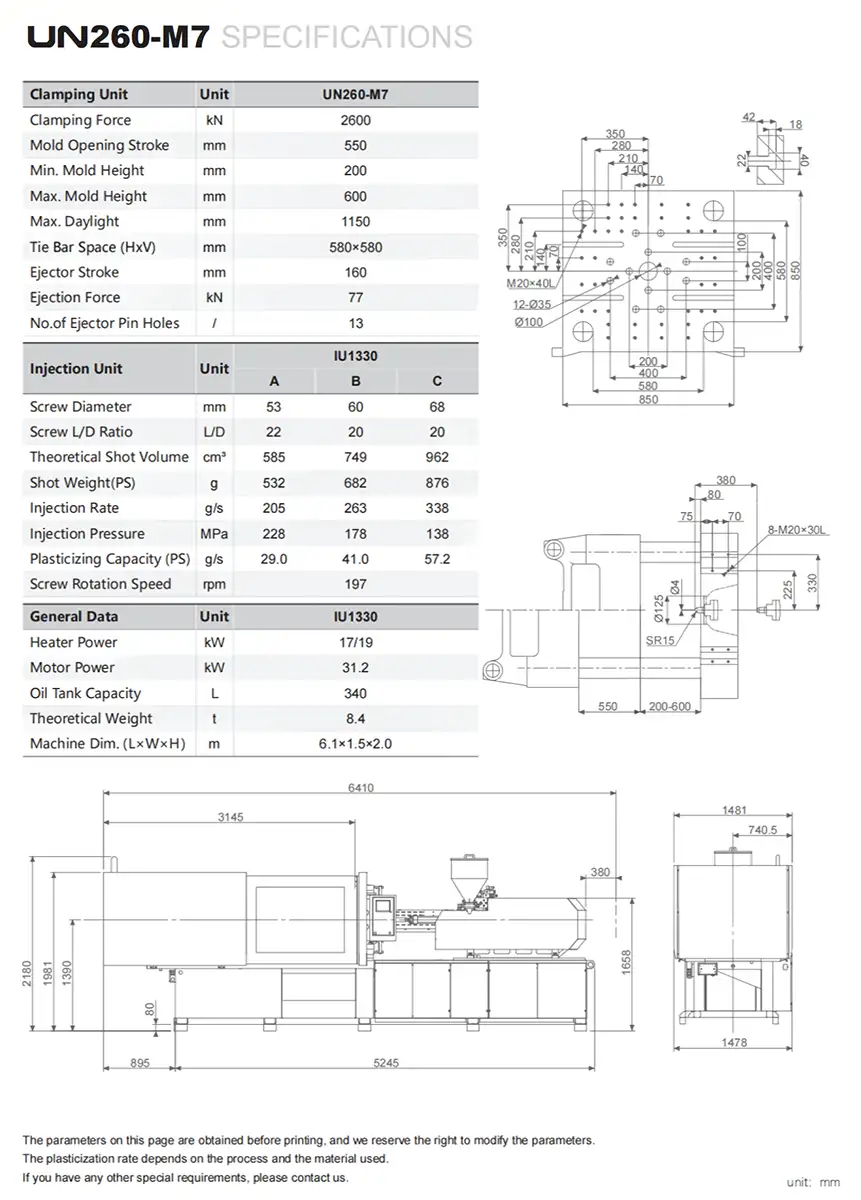
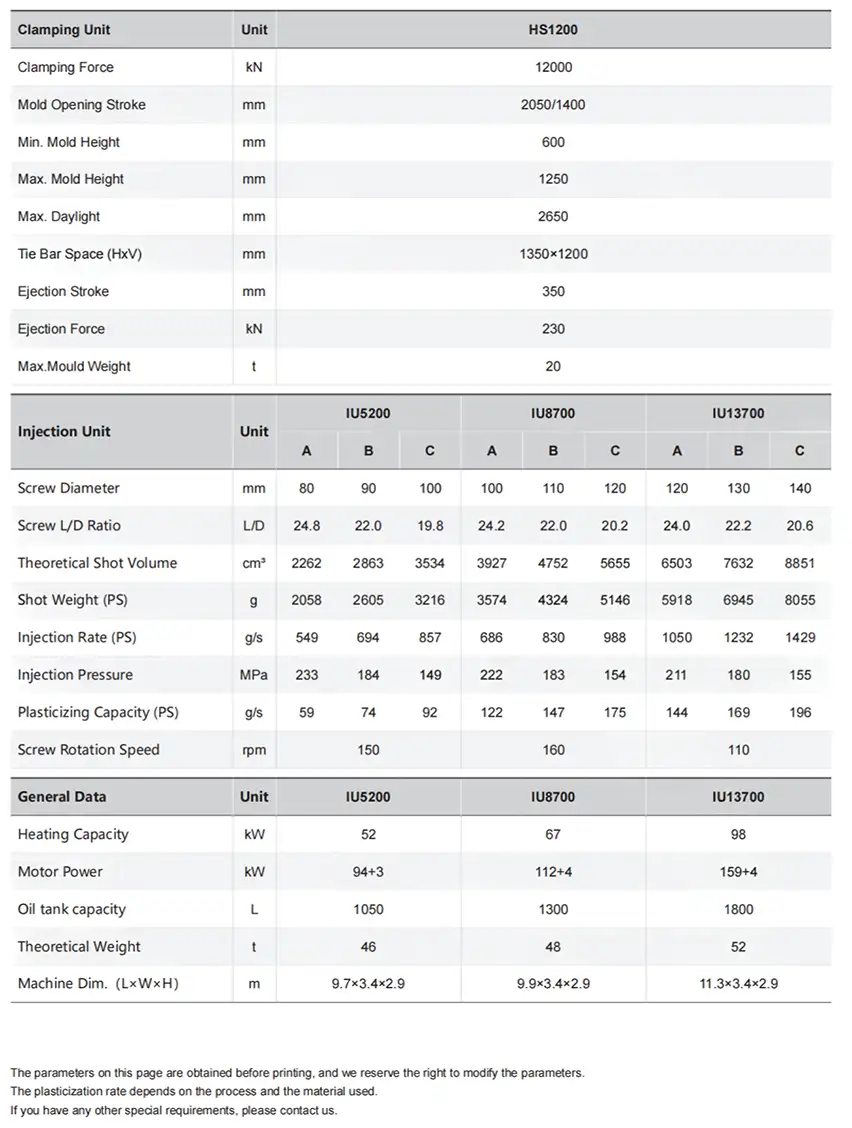
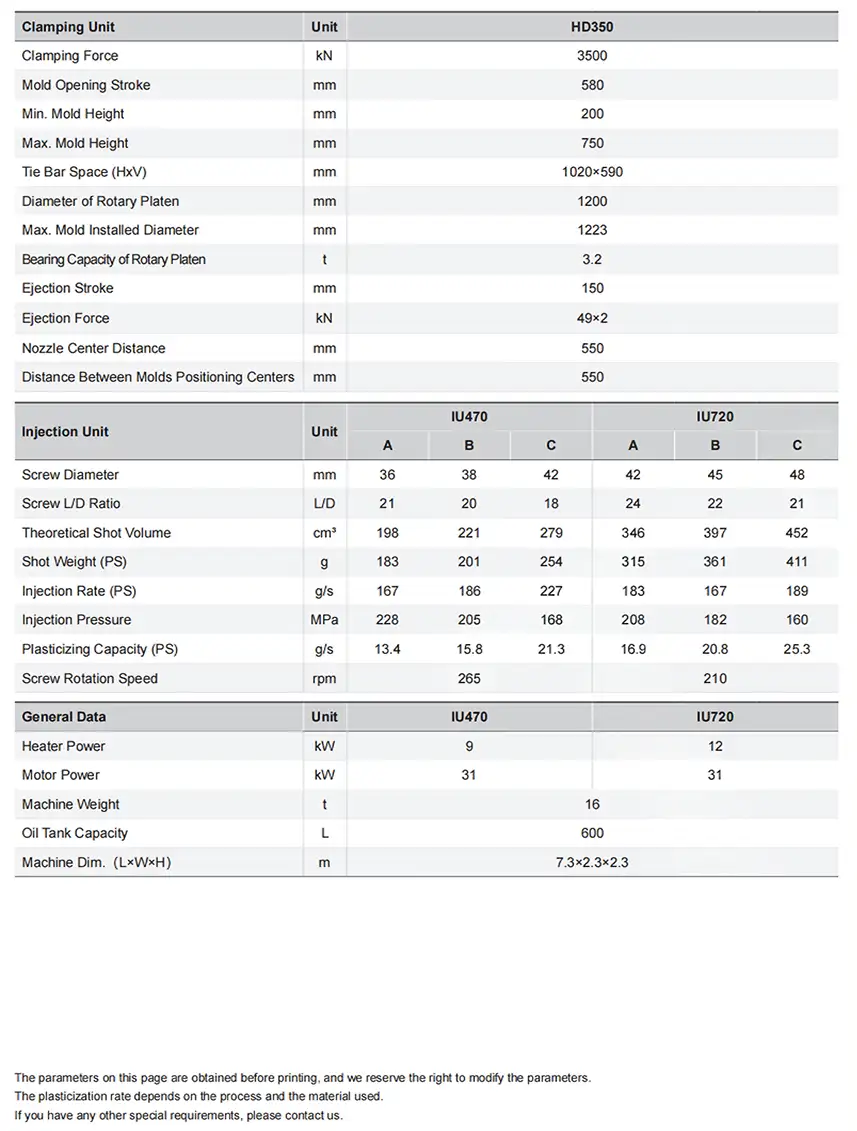
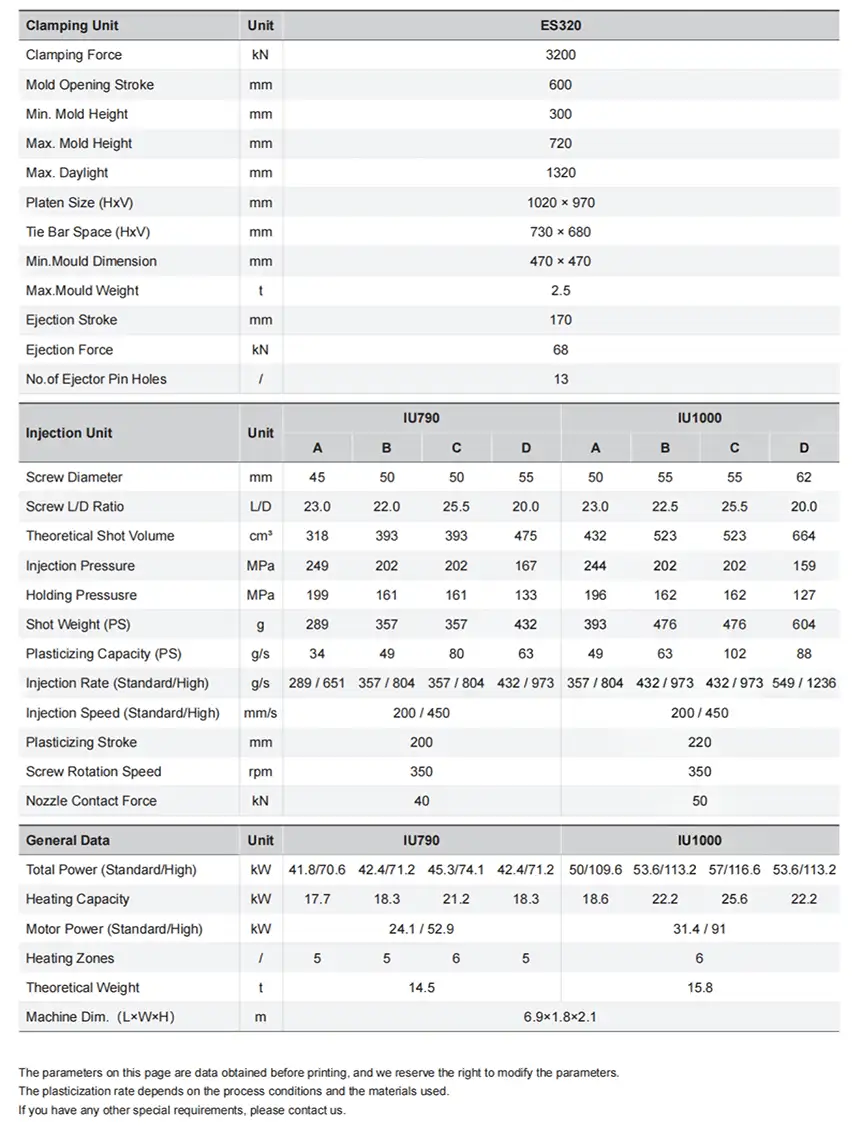
What Is a Mold Temperature Controller (TCU)?
A Mold Temperature Controller (TCU) is a dynamic, closed-loop thermal energy exchange system designed for the injection mold. It actively manages and maintains the mold surface temperature by precisely adding or removing heat. Its primary mechanism involves circulating a temperature-controlled fluid—typically water or thermal oil—through the mold’s internal channel network. This continuous, high-volume flow ensures rapid and efficient heat transfer, stabilizing the mold at an optimal, application-specific thermal setpoint crucial for achieving consistent molecular structure and part geometry.
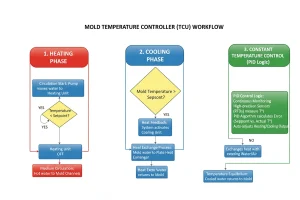
Core Components of Mold Temperature Controllers
- Energy Addition (Heating)
- High-efficiency electric immersion heaters rapidly raise the circulating fluid to the desired setpoint and maintain it during production.
- Energy Removal (Cooling)
- An integrated heat exchanger removes excess thermal energy transferred from the molten polymer, preventing temperature overshoot and enabling consistent cycle times.
- The Control Core
- High-precision sensors (such as RTDs or thermocouples) continuously monitor fluid temperature and transmit data to a microprocessor running a PID algorithm.
- This enables the controller to anticipate heat demand and automatically adjust heating or cooling output to maintain stability, typically within ±0.1°C.
- This accuracy is crucial for applications involving thin-walled parts or engineering-grade polymers, where even small temperature changes can directly impact dimensional stability.
Not sure if your temperature control is optimal?
We can analyze your current molding parameters and identify opportunities for quality improvement.
Technical Principles: From Mold Design to Flow Rate
A TCU’s effectiveness is realized through its integration with three fundamental engineering variables: mold geometry, polymer rheology, and fluid dynamics.
Mold Geometry and Heat Dissipation
Mold design dictates the uniformity of heat removal. Conventional straight-drilled channels can create uneven cooling zones, leading to differential shrinkage—a primary cause of warpage. Modern mold engineering increasingly leverages conformal cooling. These channels, often produced via additive manufacturing, trace the part’s contour to ensure a uniform heat flux. This geometric optimization can reduce cooling cycles by 15-30% compared to traditional methods.
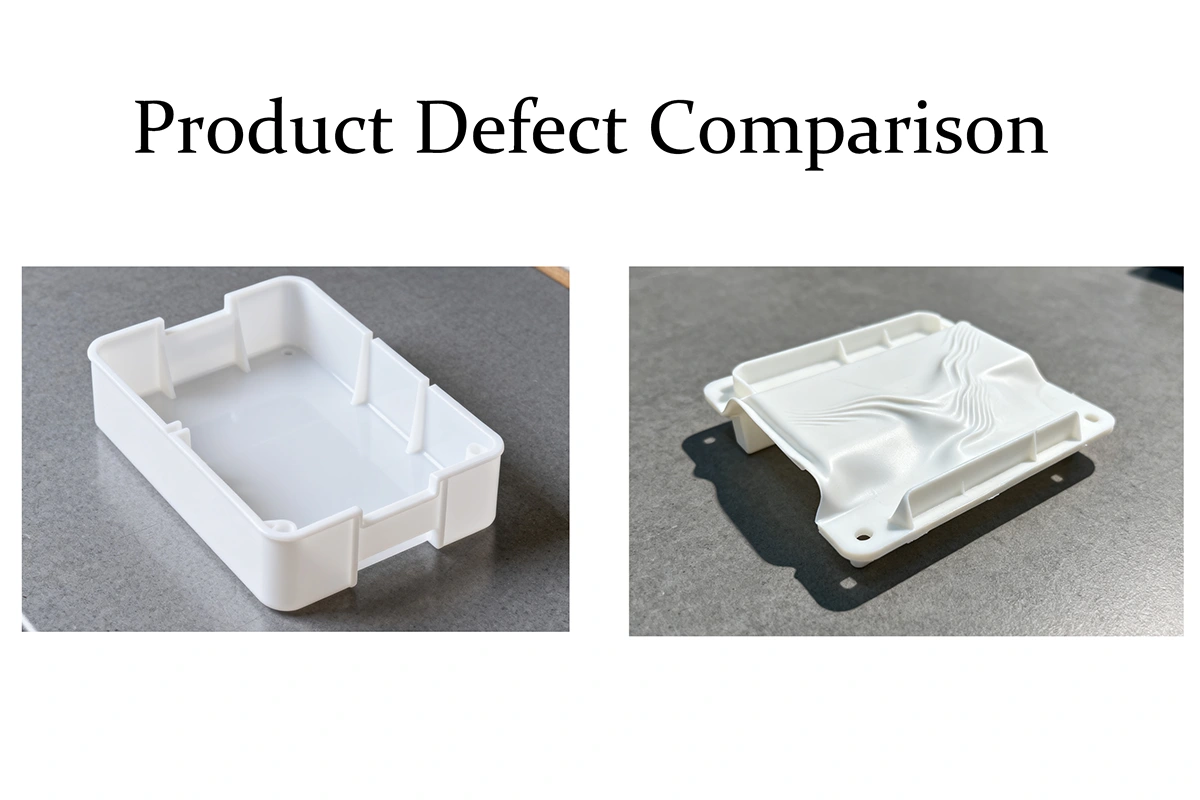
Polymer Rheology and Viscosity Control
Polymer viscosity is highly sensitive to temperature, governing its ability to fill the cavity and replicate surface details. For many engineering-grade polymers, a temperature variation of just 5°C can significantly alter the shear rate and flow front progression. By maintaining a precise thermal setpoint, the TCU ensures consistent melt viscosity, mitigating defects like short shots, weld lines, and inconsistent surface textures caused by premature gate freeze-off.
Fluid Dynamics and Cycle Optimization
Optimizing heat transfer requires balancing the cooling fluid’s dynamics. The goal is to achieve turbulent flow, indicated by a Reynolds number (Re) greater than 4000, which maximizes the convective heat transfer coefficient.
How to Choose the Right TCU
Determining the right TCU is no easy task; it’s a strategic decision that directly impacts production quality, scrap, and energy consumption. The process must be driven by the thermal requirements of the polymer and mold design.
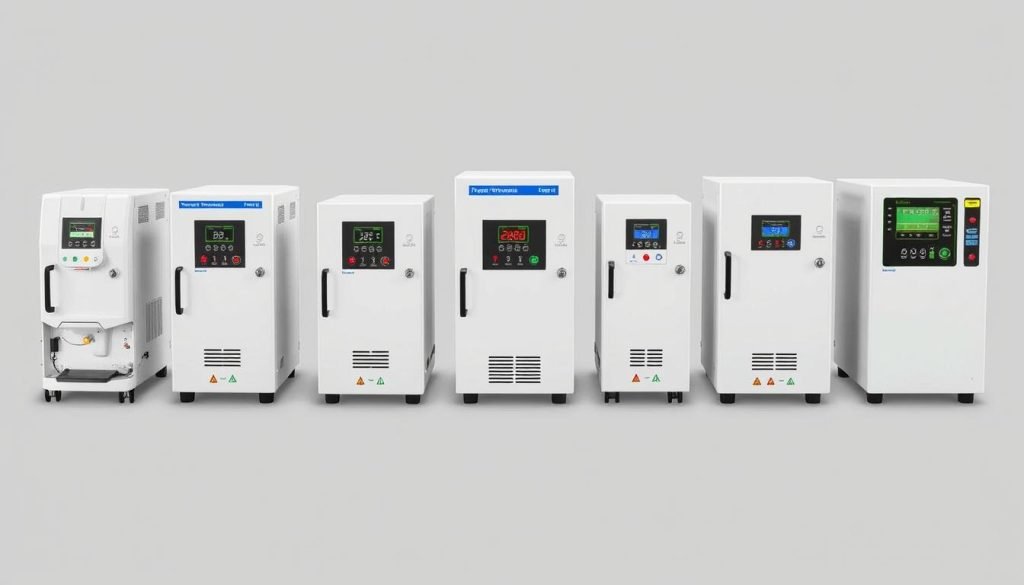

The Fundamental Choice: Circulating Medium
The first decision is the heat transfer fluid, dictated by the required operating temperature.
Essential Engineering Criteria
Once the medium is determined, the following parameters must be calculated:
- Heating/Cooling Capacity (kW): The TCU’s capacity must match the mold’s thermal load. Correct sizing prevents inefficiency from an oversized unit or slow temperature recovery from an undersized one.
- Flow Rate and Pressure: The pump must provide sufficient flow (typically 30 to 60 L/min or higher) and pressure to overcome restrictions in the mold circuit and achieve turbulent flow.
- Control Precision: For high-tolerance parts made from sensitive materials, a TCU must maintain stability of ±0.5°C or better.
Advanced Features Worth Considering
Modern TCUs offer features that integrate them into a smart manufacturing environment:
- Multi-Zone Control: Independent temperature regulation for different mold sections (e.g., core vs. cavity) to manage complex thermal gradients.
- Data Acquisition and Logging: Records of temperature, flow, and pressure for ISO compliance and quality assurance traceability.
- Predictive Diagnostics: Early-warning alerts for pump or heater degradation to minimize unplanned downtime.
- System Integration: Communication protocols like OPC UA or Ethernet for seamless integration with a Manufacturing Execution System (MES).
Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance of mold temperature controllers is essential for consistent performance and longevity. A well-maintained TCU can provide years of reliable service, while neglected units often lead to quality issues and production downtime.
Common TCU Issues and Quick Fixes
| Problem | Possible Causes | Quick Fix |
| Temperature Fluctuations | Clogged filter, air in system, failing sensor | Clean/replace filter, purge air from system, check sensor calibration |
| Insufficient Flow Rate | Pump wear, clogged channels, closed valves | Check pump operation, clean system with descaling agent, verify valve positions |
| Leaking Connections | Worn gaskets, loose fittings, thermal expansion | Replace gaskets, tighten connections, use flexible hoses rated for temperature |
| Heater Failure | Scale buildup, electrical issues, overheating | Descale heating elements, check electrical connections, verify flow before heating |
| Control System Errors | Software glitches, sensor issues, power fluctuations | Restart controller, check sensor connections, install power conditioning |
Preventative Maintenance Schedule
Daily Checks
- Verify fluid levels and top up if necessary
- Check for leaks around connections
- Monitor pressure and temperature readings
Weekly Tasks
- Clean external filters
- Inspect hoses for wear or damage
- Check pump operation and unusual noises
Monthly Maintenance
- Clean internal filters and strainers
- Check electrical connections for tightness
- Calibrate temperature sensors if necessary
Quarterly Service
- Descale heating elements and cooling circuits
- Check pump seals and replace if worn
- Verify control system accuracy
Pro Tip: Water Quality Management
Water quality is critical for water-based TCUs. Use distilled or properly treated water to prevent scale buildup and corrosion. Consider installing a closed-loop water treatment system for optimal performance and extended equipment life.
Conclusion

Ready to optimize your molding process?
Our experts can provide the right TCU for your needs.